Variation of Moisture Content as a Parameter of Study by Induced Polarization Technique in Soil Sample of Coastal Andhra Pradesh
Abstract
By using non-destructive methods such as induced polarization (IP) based on indigenous equipment; experimental data has been collected to find relations of chargeability/resistivity and moisture content. The same techniques are applicable to other parameters such as CEC and grain size. Induced polarization technique based upon time domain methods can be used for studying the parameters of soil mechanics. Moisture content is a common quality which cannot be properly studied by electrical resistivity techniques. Chargeability of soil is directly related to moisture content. The chargeability is expressed (*) where Vp is ON-time measured voltage and Vsis the OFF-time measured voltage. Measurements are made of the decay of Vs over a short time period (0.1s) after some discreet intervals of time. The value of m is calculated from the integration techniques.
*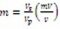
Keywords
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License.

